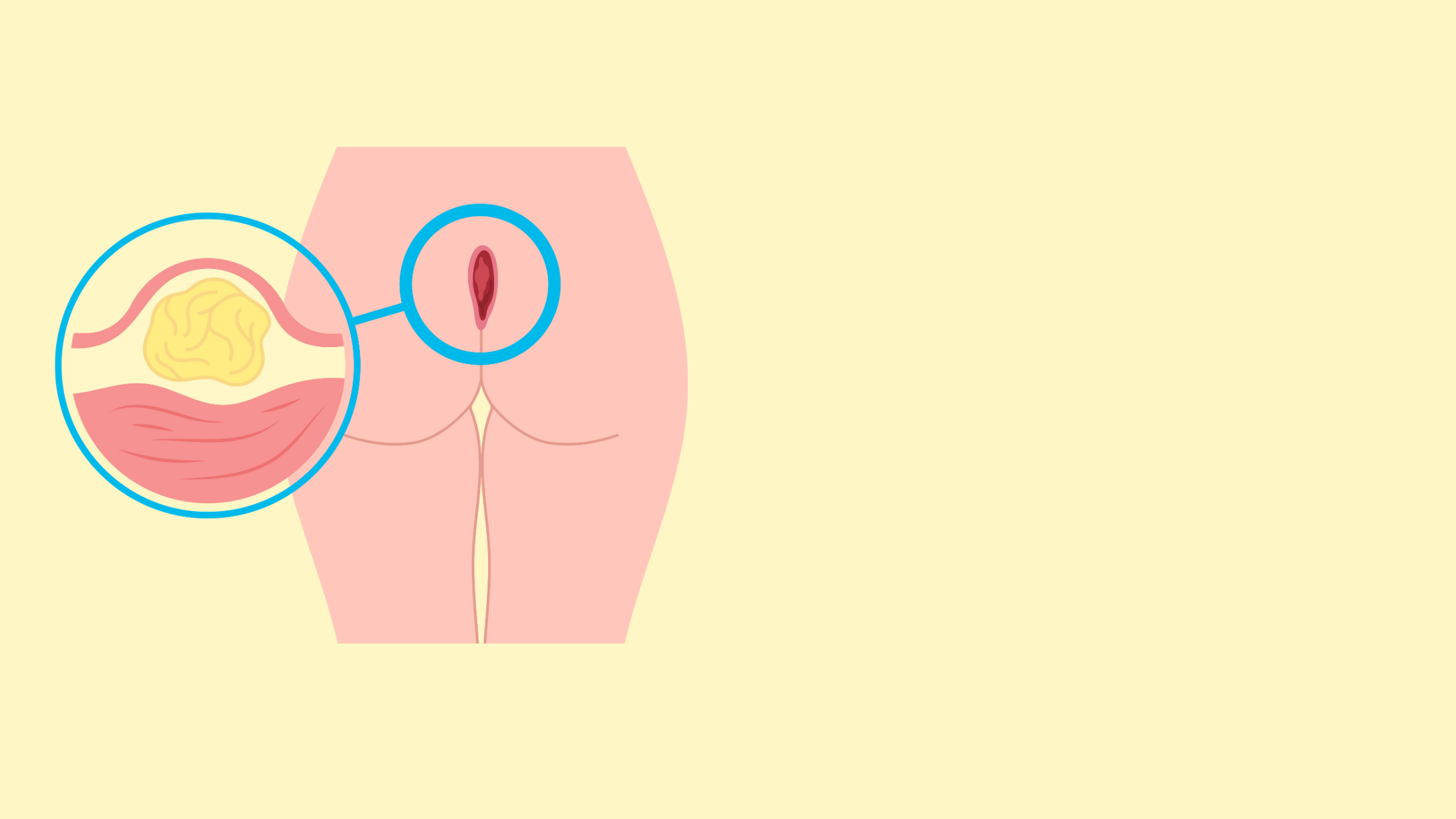
Pilonidal disease is a condition in which a cyst or abscess forms in the crease between the buttocks, near the tailbone. In this essay, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for pilonidal disease.
The exact cause of this disease is unknown, but it is believed to be caused by hair follicles that become embedded in the skin, leading to infection and inflammation. The hair follicles may become inflamed due to pressure, friction, or ingrown hairs, causing the formation of a cyst or abscess.
Other factors that may increase the risk of developing pilonidal disease include:
- obesity
- a sedentary lifestyle
- family history of pilonidal disease
The symptoms of pilonidal disease may vary depending on the severity of the condition. In the early stages, patients may experience mild pain and swelling in the area between the buttocks. As the condition progresses, the pain may become more severe and may be accompanied by a discharge of pus or blood from the cyst. Patients may also experience fever and fatigue, indicating a more severe infection.
The treatment of pilonidal disease will depend on the severity of the condition. In mild cases, the cyst may be drained and the area may be treated with antibiotics to prevent infection. In some cases, a patient may benefit from hair removal to remove hair from the affected area and reduce the risk of recurrence.
In more severe cases or recurrent disease, surgery may be required to remove the cyst and any infected tissue. There are several surgical options available, including excisional surgery, which involves removing the cyst and any surrounding tissue, and removal and repair surgery, which involves using healthy tissue to cover the wound and promote healing. This is sometimes referred to as “cleft elevation” surgery, which involves limited excision and recontouring the skin of the buttock crease. These leads to quicker recovery, less pain, easier post-operative care and decreased chance of pilonidal recurrence. Cleft-elevation surgery is generally performed by surgeons who have developed special expertise in this type of surgery.
There are several steps that can be taken to prevent pilonidal disease. Maintaining good hygiene and keeping the area between the buttocks clean and dry can help prevent infection. Patients should also avoid sitting for long periods of time, as this can increase pressure on the area and lead to the development of a cyst. In addition, patients who are prone to developing pilonidal disease may benefit from hair removal or laser hair removal to reduce the risk of hair follicles becoming embedded in the skin.
In conclusion, pilonidal disease is a condition that affects the skin in the crease between the buttocks and is caused by hair follicles becoming embedded in the skin. The symptoms may range from mild pain and swelling to severe pain and the formation of a cyst or abscess. Treatment options include draining the cyst, antibiotics, and surgery, depending on the severity of the condition. Prevention measures include maintaining good hygiene, avoiding sitting for long periods of time, and hair removal or laser hair removal. If you suspect you may have pilonidal disease, it is important to see a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
